Cayman Chemical Co.
Human Cannabinoid Type 1 Receptor Reporter Assay System, 96 wells, Item No. 34256
- SKU:
- CAY-34256-96wells
Description
Human Cannabinoid Type 1 Receptor Reporter Assay System, 96 wells, Item No. 34256
Product Description
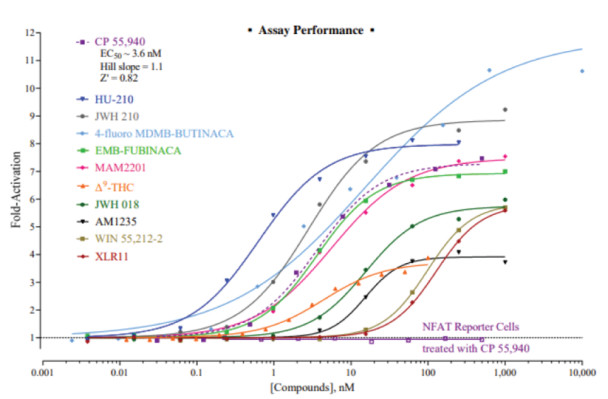
This assay uses proprietary human cells that provide constitutive expression of the Human Cannabinoid Type 1 Receptor, also referred to as CB1R.
CB1R is one of the two main cannabinoid receptors identified as part of the endocannabinoid system. CB1R is highly expressed in the central nervous system, but also in skeletal muscles, gastrointestinal tract, liver, pancreas, skin, reproductive system, and cardiovascular system. The CB1R is involved in a wide range of physiological and pathophysiological processes related to neurological disorders, energy metabolism, obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular and reproductive disorders, inflammation, and cancer.
CB1R is a member of the super-family of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCR). Its structure includes seven transmembrane helices, with an extracellular amino end and an intracellular carboxy tail associated with trimeric G proteins. Upon ligand binding, the receptor undergoes conformational change that triggers the activation of G proteins via an exchange of GDP to a GTP.
Modes of CB1R signal transduction are diverse and may involve a variety of signaling molecules and kinases that vary based on the type of ligand and the type of cells in which the receptor is expressed. The first signaling pathway described for CB1R involved activation of a pertussis toxin sensitive G protein (Gαi/o), leading to the inhibition of forskolin-stimulated cyclic AMP, activation of G protein-coupled inwardly rectifying potassium channels (GIRKs), and an inhibition of several calcium channels. This is followed by recruitment of β-arrestin, a cytosolic protein involved in receptor desensitization and internalization. However, β-arrestin activation is also involved in the activation of downstream kinases such as MAPK.
CBIR can also couple with stimulatory G proteins such as Gαs and Gαq/11, resulting in the activation of ERK and PLC pathways and increased levels of intracellular calcium. An outcome of CB1R activation is that calcineurin, a calcium-dependent phosphatase, dephosphorylates and activates the transcription factor NFAT. Signal transduction via the Ca+2-calcineurin / NFAT cascade is exploited by the reporter cells used in this assay.
INDIGO's Reporter Cells contain an engineered luciferase reporter gene functionally linked to tandem NFAT genetic response elements (GRE) and a minimal promoter. Activated NFAT binds to its corresponding GREs to initiate the formation of a complete transcription complex that drives Luc gene expression. Quantifying changes in luciferase activity in the treated reporter cells relative to the untreated cells provides a sensitive, dose-dependent surrogate measure of drug-induced changes in CB1R activity. Accordingly, the principal application of this reporter assay is in the screening of test compounds to quantify any functional activities, either activating or inhibitory, that they may exert against CB1R or its associated calcineurin-NFAT signal transduction pathway.
[INDIGO Catalog Nos. IB19001-32, IB19001, IB19002]
WARNING This product is not for human or veterinary use.
Technical Information
- Cannabinoid Receptor 1
- CANN6
- CB1
- CB1A
- CB1K5
- CB1R
- CB-R
- CNR
- CNR1
Shipping & Storage Information
Certificates of Analysis & Batch Specific Data
Get Batch-Specific Data and Documents by Batch Number
Provide batch numbers separated by commas to download or request available product inserts, QC sheets, certificates of analysis, data packs, and GC-MS data.