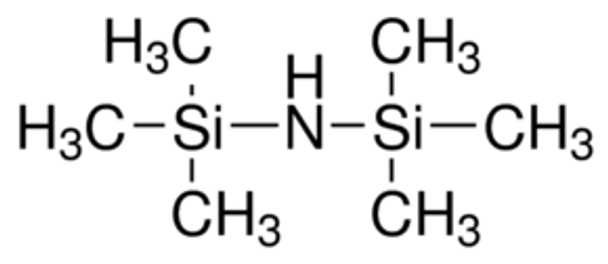General description
Hexamethyldisilazane (HMDS) is a commercially available, silylating agent,[1][2] which is used as an alternative for the preparation of silyl ethers from hydroxyl compounds.[2]
Application
Learn more in the Product Information
Hexamethyldisilazane is suitable for the derivatization of alcohols, U-aminobutyric acid, pesticidal carbamates and urea, 3,4-Dihydroxyphenylglycol, 4-hydroxycoumarins, hydroxyfatty acids, n-hydroxy-2-fluorenylacetamide, kerb cycle acid, malonaldehyde, monoglycerides, phenylpyruvic acid, shikimic acid, unsaturated fatty acid esters (or methyl esters), and related compounds.
It may be used as a derivatizing reagent for the analysis of bioamines and their acidic metabolites,[3] phenol, hydroquinone and catechol[4] in urine samples, mixtures of free fatty acids and metal soaps in paint samples[5] using gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (GC/MS).
Suitable for the derivatization of alcohols, Υ-aminobutyric acid, pesticidal carbamates and urea, 3,4-Dihydroxyphenylglycol, 4-hydroxycoumarins, hydroxyfatty acids, n-hydroxy-2-fluorenylacetamide, kerb cycle acid, malonaldehyde, monoglycerides, phenylpyruvic acid, shikimic acid, unsaturated fatty acid esters (or methyl esters), and related compounds.
Other Notes
Important silylating agent[6][7]
Reagent for 2-hydroxypyrimidine, polytrimethylsilyloxy, trimethylsilyl and trimethylsilyl oximes.