Description
Arachidonic acid, 50MG
analytical standard
Synonym(s):
Immunocytophyte, Eicosa-5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z-tetraenoic acid, cis,cis,cis,cis-5,8,11,14-Eicosatetraenoic acid
Linear Formula:
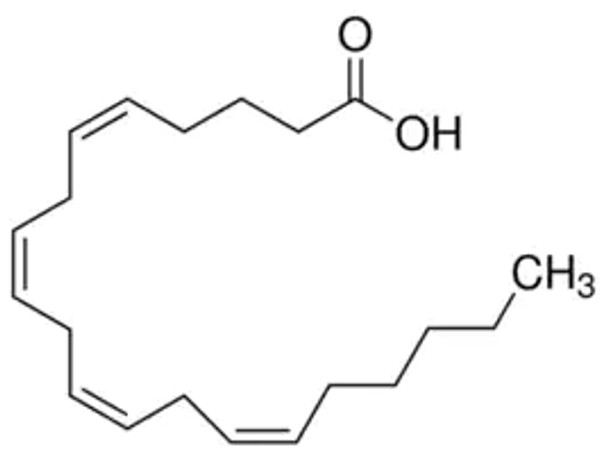
CH3(CH2)4(CH=CHCH2)4CH2CH2CO2H
CAS Number:
506-32-1
Molecular Weight:
304.47
Beilstein:
1713889
EC Number:
208-033-4
MDL number:
MFCD00004417
PubChem Substance ID:
329752420
NACRES:
NA.24
PROPERTIES
Quality Level
100
biological source
synthetic
grade
analytical standard
assay
≥97.0% (GC)
form
liquid
shelf life
limited shelf life, expiry date on the label
refractive index
n20/D 1.4872 (lit.)
bp
169-171 °C/0.15 mmHg (lit.)
mp
−49 °C (lit.)
density
0.922 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
application(s)
food and beverages
format
neat
functional group
carboxylic acid
storage temp.
2-8°C
SMILES string
OC(CCC/C=C\C/C=C\C/C=C\C/C=C\CCCCC)=O
InChI
1S/C20H32O2/c1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-15-16-17-18-19-20(21)22/h6-7,9-10,12-13,15-16H,2-5,8,11,14,17-19H2,1H3,(H,21,22)/b7-6-,10-9-,13-12-,16-15-
InChI key
YZXBAPSDXZZRGB-DOFZRALJSA-N
DESCRIPTION
Biochem/physiol Actions
Arachidonic acid stimulates adhesion of MDA-MB-435 human metastatic cancer cells to extracellular matrix molecules (collagen IV and vitronectin) .
Arachidonic acid (AA) is an unsaturated ω6 fatty acid constituent of the phospholipids of cell membranes. Phospholipase A2 releases AA from the membrane phospholipids in response to inflammation. AA is subsequently metabolized to prostaglandins and thromboxanes by at least two cyclooxygenase (COX) isoforms, to leukotrienes and lipoxins by lipoxygenases, and to epoxyeicosatrienoic acids via cytochrome p450-catalyzed metabolism. AA and its metabolites play important roles in a variety of biological processes, including signal transduction, smooth muscle contraction, chemotaxis, cell proliferation and differentiation, and apoptosis. AA has been demonstrated to bind to the a subunit of G protein and inhibit the activity of Ras GTPase-activating proteins (GAPs). Cellular uptake of AA is energy dependent and involves protein-facilitated transport across the plasma membrane.
SAFETY INFORMATION
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
235.4 °F - closed cup
Flash Point(C)
113 °C - closed cup