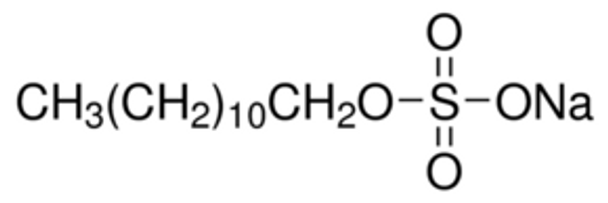Description
Sodium dodecyl sulfate ACS reagent, ≥99.0%, 100G
Synonym: Dodecyl sodium sulfate, Dodecyl sulfate sodium salt, Lauryl sulfate sodium salt, SDS, Sodium lauryl sulfate
-
CAS Number 151-21-3
-
Linear Formula CH3(CH2)11OSO3Na
-
Molecular Weight 288.38
-
Beilstein/REAXYS Number 3599286
-
EC Number 205-788-1
-
MDL number MFCD00036175
-
eCl@ss 39093306
-
PubChem Substance ID 24867284

-
NACRES NA.21
Properties
| Related Categories | Alkyl Sulfates, Anionic Detergents, Antigen-Vaccine Preparation, Biochemicals and Reagents, Building Blocks, Cell Culture, Chemical Synthesis, Core Bioreagents, Denaturation, Detergents, Detergents N to Z, Detergents by Applications, Diagnostic Applications, Drug Delivery-Liposomes, Electrophoresis Chromatography, Enzymology, Membrane Protein Solubilization, Organic Building Blocks, Organic Sulfates/Sulfites, Research Essentials, Sulfur Compounds Less... |
| Quality Level | 200 |
| grade | ACS reagent |
| description | anionic |
| assay | ≥99.0% |
| mol wt | 288.38 g/mol |
| description | 62 |
| impurities | ≤0.06 meq/g Titr. Base |
| - | ≥96.0% fatty alcohols |
| - | <4.0% unsulfated alcohols |
| loss | ≤1.0% loss on drying |
| mp | 204-207 °C (lit.) |
| solubility | H2O: soluble 1 gm in 10 ml (opalescent solution) |
| cation traces | heavy metals (as Pb): ≤0.002% |
| λ | 3 %H2O reference |
| UV absorption | λ: 220-350 nm Amax: ≤0.1 |
| HLB | 40 |
| SMILES string | [Na+].CCCCCCCCCCCCOS([O-])(=O)=O |
| InChI | 1S/C12H26O4S.Na/c1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-16-17(13,14)15;/h2-12H2,1H3,(H,13,14,15);/q;+1/p-1 |
| InChI key | DBMJMQXJHONAFJ-UHFFFAOYSA-M |
Application
Sodium dodecyl sulfate was used as a test compound for studying that whether Bacillus amyloliquefaciens KPS46 can induce priming, signaling, protein production as well as systemic protection in soybean (Glycine max L.) against several diseases.[2]
Anionic detergent
Packaging
25, 100 g in poly bottle
Biochem/physiol Actions
Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) is an anionic detergent that can form complexes with protein through hydrophobic interactions. Studies have reported that the hydrodynamic functions of protein-SDS complexes are governed by the length of their polypeptide chains. Thus, SDS-based electrophoretic techniques can separate protein molecules based on their molecular weights.[3] Additionally, SDS can solubilize cell membranes and can extract membrane-bound proteins.[1]
Safety Information