Description
Salicylic acid ACS reagent, ≥99.0%, 100G
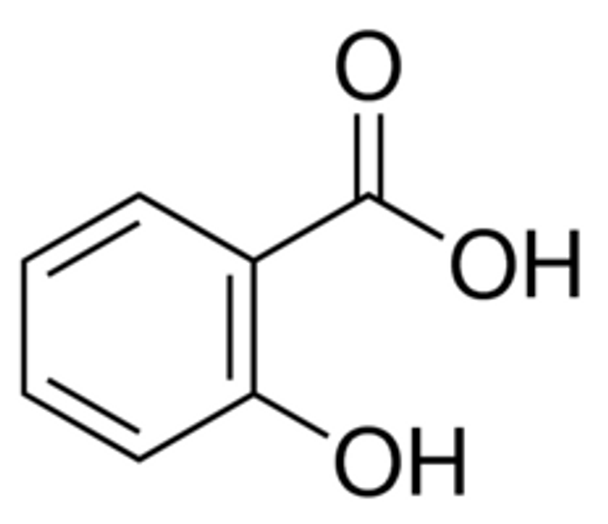
Synonym: 2-Hydroxybenzoic acid
-
CAS Number 69-72-7
-
Linear Formula 2-(HO)C6H4CO2H
-
Molecular Weight 138.12
-
Beilstein/REAXYS Number 774890
-
EC Number 200-712-3
-
MDL number MFCD00002439
-
PubChem Substance ID 24854876
Properties
| Related Categories | Acids, Acids & Bases, Aromatic Compounds, Building Blocks, C7, Carbonyl Compounds, Carboxylic Acids, Cell Biology, Chemical Synthesis, Nutrition Research, Organic Acids, Organic Building Blocks, Phytochemicals by Chemical Classification, Synthetic Reagents Less... |
| Quality Level | 200 |
| grade | ACS reagent |
| vapor density | 4.8 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 1 mmHg ( 114 °C) |
| assay | ≥99.0% |
| impurities | H2SO4, passes test (darkened) |
| ign. residue | ≤0.01% |
| bp | 211 °C (lit.) |
| mp | 158-161 °C (lit.) |
| anion traces | chloride (Cl-): ≤0.001% |
| - | sulfate (SO42-): ≤0.003% |
| cation traces | Fe: ≤2 ppm |
| - | heavy metals (as Pb): ≤5 ppm |
| storage temp. | room temp |
| SMILES string | OC(=O)c1ccccc1O |
| InChI | 1S/C7H6O3/c8-6-4-2-1-3-5(6)7(9)10/h1-4,8H,(H,9,10) |
| InChI key | YGSDEFSMJLZEOE-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Gene Information | human ... ALB(213), PTPN1(5770) |
General description
Salicylic acid is mainly used as the precursor to synthesize aspirin, a commonly used analgesic and antipyretic.[5] Due to its keratolytic action, it is also used in topical ointments.[6]
Application
Salicylic acid has been used:
• to study its antimicrobial effect in vitro and in situ against Penicillium expansum[11]
• as one of the chemical compound in exposure-based validation of in vitro gastrulation model employed in developmental toxicity screening assays[12]
• as a reference standard in salicylate quantification by reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC)[13]
Packaging
100, 500 g in poly bottle
Biochem/physiol Actions
Salicylic acid (SA) delivers local and systemic acquired resistance (LAR and SAR) against various diseases in plants.[9] It acts as a secondary metabolite and regulate various physiological processes such as, seed germination, seedling establishment, cell growth, respiration, stomatal closure and senescence-associated gene expression. In addition, SA also controls abiotic stress, basal thermotolerance, nodulation in legumes and fruit yield. It plays a vital role in modulation of flowering and thermogenesis (heat production) in plants. SA together with reactive oxygen species (ROS) and nitric oxide (NO) triggers cell death in plants.
Safety Information