Description
Kinetin
suitable for plant cell culture, BioReagent, amorphous powder
Synonym: 6-Furfurylaminopurine, N6-Furfuryladenine
-
CAS Number 525-79-1
-
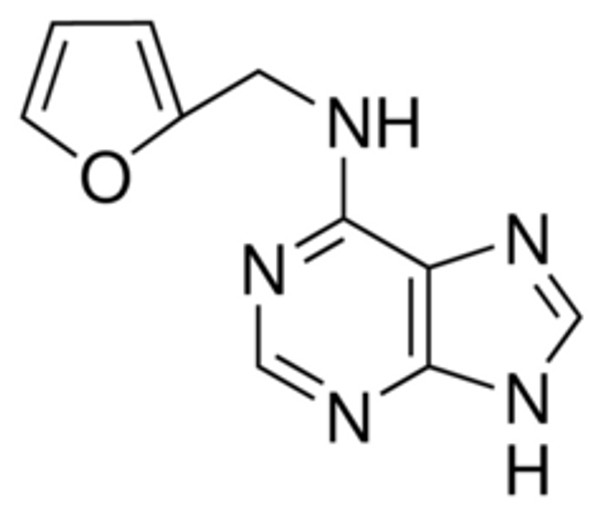
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation) C10H9N5O
-
Molecular Weight 215.21
-
Beilstein/REAXYS Number 21703
-
EC Number 208-382-2
-
MDL number MFCD00075757
-
PubChem Substance ID 24896230
-
NACRES NA.72
Properties
| Related Categories | Cytokinins, Molecular Biology, Plant Biotechnology, Plant Growth Regulators, Plant Tissue Culture Less... |
| Quality Level | 200 |
| product line | BioReagent |
| assay | ≥98% (TLC and HPLC) |
| form | amorphous powder |
| application(s) | cell culture | plant: suitable |
| color | off-white |
| mp | 264-270 °C (dec.) (lit.) |
| Featured Industry | Agriculture |
| SMILES string | C(Nc1ncnc2[nH]cnc12)c3ccco3 |
| InChI | 1S/C10H9N5O/c1-2-7(16-3-1)4-11-9-8-10(13-5-12-8)15-6-14-9/h1-3,5-6H,4H2,(H2,11,12,13,14,15) |
| InChI key | QANMHLXAZMSUEX-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
General description
Kinetin is a cell division factor or cytokinin from DNA.[1][6] It occurs naturally in various plant extracts such as those from coconuts, maize endosperm, banana and horsechestnut fruits, carrot and tobacco leaves, grapes, crown gall tumors, female gametophytes of Ginkgo and many other sources.[2]
Application
Kinetin has been used as a supplement in modified MS medium for culturing various plant tissues.[4][5] It has also been used to study its effect on thymus and immune function of aging rats.[6]
Packaging
1 g in poly bottle
5, 25 g in glass bottle
Biochem/physiol Actions
Kinetin has an ability to induce cell division differentiation and growth. In addition, it also acts as an antioxidant and delays the aging process.[6] Kinetin acts as a potential tool for studying effects of red light on plants.[3]
Kinetin is an adenine-type cytokinin phytohormone that is used in plant culture media such as Murashige & Skoog media in conjunction with auxins such as indole-3-acetic acid (IAA), Indole-3-butyric acid (IBA), 1-napthaleneacetic acid (NAA) or others to induce the fomation of callus and to regenerate plant tissues from callus.