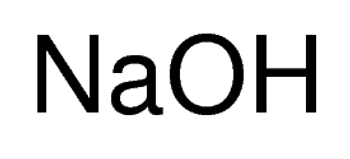Description
221465 Sigma-Aldrich
Sodium hydroxide
ACS reagent, ≥97.0%, pellets
Synonym: ‘Caustic soda’
-
CAS Number 1310-73-2
-
Linear Formula NaOH
-
Molecular Weight 40.00
-
EC Number 215-185-5
-
MDL number MFCD00003548
-
PubChem Substance ID 329752270
-
NACRES NA.21
Description
General description
Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) also known as caustic soda is a water soluble inorganic base with a wide range of industrial application such as titration,[12] dissolution testing[13] and in impinger to remove acidic gases.[8] It participates in the oxidation of glycerol catalyzed by Au/charcoal or Au/graphite.[4] It participates in solvent-free aldol condensation reaction.[7]
Application
Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) was used in the following processes:
• Preparation of sodium 3,3′-bis(sulfonato)-4,4′-bis(chloroacetamido)azobenzene (BSBCA) that is utilized in protein cross-linking techniques.[2]
• Preparation of electrolyte solution to study the effect of electrolyte composition on the conversion of CO2 to CO by electrochemical reduction.[9]
• Preparation of CSK (cytoskeleton) buffer for the three-dimensional (3D) slide method of preserving the 3D chromatin structure of testicular germ cells.[10]
• Synthesis of ZSMs (zeolite socony mobils).[11]
Sodium hydroxide may be employed for the deterimination of specific surface area of colloidal silica, via titration.[5] It may be employed for the direct oxidation of sodium borohydride, which was investigated by cyclic and linear voltammetry, chronoamperometry and chronopotentiometry.[6] It may be used to prepare citrate buffer and borate buffer.[1] It may be used in the synthesis of :
• alkylaryl amidosulfobetaines[3]
• (3 -[4-teroctylphenoxyethoxyethoxyethyl] dimethylammonio propane sulfonate (XOSB)[3]
• trisulfobetaines (TriSBn)[3]
Sodium hydroxide may be used as a base in titration methods[12], dissolution testing[13], for adjusting pH[14] and in the impinger to remove acidic gases.[12]
It may be used in the following processes:
• Conversion of glycerol to glyceric acid in the presence of gold catalyst.[15]
• Palladium-catalyzed cross-coupling reaction between vinylalkoxysilanes and aryl bromides or chlorides to form styrenes.
Packaging
1, 2.5 kg in poly bottle
12, 25, 50 kg in poly drum
25, 500, 6×500 g in poly bottle
Properties
| Related Categories | ACS Grade Acids & Bases, Acids & Bases, Acids and Bases, Adsorbents, Filter Aids and Drying Agents, Analytical Reagents, |
| Quality Level | 200 |
| grade | ACS reagent |
| vapor density | >1 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | <18 mmHg ( 20 °C) |
| 3 mmHg ( 37 °C) | |
| assay | ≥97.0% |
| form | pellets |
| impurities | ≤0.001% N compounds |
| ≤0.02% NH4OH ppt. | |
| ≤1.0% Na2CO3 | |
| mp | 318 °C (lit.) |
| solubility | water: soluble 1,260 g/L at 20 °C |
| anion traces | chloride (Cl-): ≤0.005% |
| phosphate (PO43-): ≤0.001% | |
| sulfate (SO42-): ≤0.003% | |
| cation traces | Fe: ≤0.001% |
| Hg: ≤0.1 ppm | |
| K: ≤0.02% | |
| Ni: ≤0.001% | |
| heavy metals (as Ag): ≤0.002% | |
| SMILES string | [OH-].[Na+] |
| InChI | 1S/Na.H2O/h;1H2/q+1;/p-1 |
| InChI key | HEMHJVSKTPXQMS-UHFFFAOYSA-M |