Description
Retinol
synthetic, ≥95% (HPLC), crystalline
Synonym: Axerophthol, Vitamin A alcohol, Vitamin A, Vitamin A1, all-trans-3,7-Dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)-2,4,6,8-nonatetraen-1-ol
-
CAS Number 68-26-8
-
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation) C20H30O
-
Molecular Weight 286.45
-
Beilstein/REAXYS Number 403040
-
EC Number 200-683-7
-
MDL number MFCD00001552
-
eCl@ss 34058018
-
PubChem Substance ID 24899395
-
NACRES NA.79
Properties
| Related Categories | Antitumor Agents, Biochemicals and Reagents, Cancer Research, Carotenoid, Cell Biology,
Cofactor, Gene Regulation, Isoprenoid, Isoprenoids, Lipids, Metabolic Pathways, Metabolites and Cofactors on the Metabolic Pathways Chart, Metabolomics, Nutrition Research, Phytochemicals by Chemical Classification, Prenols, Vitamin A, Vitamins
|
| Quality Level | 200 |
| biological source | synthetic |
| assay | ≥95% (HPLC) |
| form | crystalline |
| application(s) | HPLC: suitable |
| color | faint yellow to very dark yellow |
| mp | 61-63 °C (lit.) |
| ε (extinction coefficient) | 2700 u/mg at 326 nm in isopropanol |
| shipped in | dry ice |
| storage temp. | −20°C |
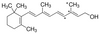
| SMILES string | CC1(C)C(/C=C/C(C)=C/C=C/C(C)=C/CO)=C(C)CCC1 |
| InChI | 1S/C20H30O/c1-16(8-6-9-17(2)13-15-21)11-12-19-18(3)10-7-14-20(19,4)5/h6,8-9,11-13,21H,7,10,14-15H2,1-5H3/b9-6+,12-11+,16-8+,17-13+ |
| InChI key | FPIPGXGPPPQFEQ-OVSJKPMPSA-N |
General description
Retinol or vitamin A alcohol is the main circulating form of vitamin A. It is not biologically active. Retinol or all-trans-retinol is a 20-carbon molecule with cyclohexenyl ring, a side chain with four double bonds (in trans configuration), and an alcohol end group.[6]
Application
Retinol has been used:
• for the synthesis of all-trans-retinoic acid in HepG2 cells[2]
• to study the effect of retinol on the growth of murine normal colonic cells cultured as organoids[3]
• as a standard for determination of vitamin A in cells[4]
• as a component of chemically defined medium for testis organ culture and spermatogenesis in vitro.[5]
Packaging
1 g in ampule
100, 250, 500 mg in ampule
Biochem/physiol Actions
Retinol and its derivatives exhibit anti-aging properties. In addition, it also acts as an anti-wrinkle agent. However, due to its photoinstability and skin irritation potency, it is not widely used in cosmetic formulations.[7] Retinol is used in the treatment of dermatoses including photoaging. Its deficiency is associated with the development of xerosis and follicular hyperkeratosis.[6]
Retinol works as a precursor of active retinoids. It is converted to retinaldehyde and subsequently to retinoic acid. All-trans and 9-cis-retinoic acid are the ligands for nuclear receptors, retinoic acid receptors (RARs) and retinoid X receptors (RXRs). These receptors are transcriptional regulators of various genes.[1]
Packaging
Bottomless glass bottle. Contents are inside inserted fused cone.
Light protecting glass vial.
Other Notes
Tandem Mass Spectrometry data independently generated by Scripps Center for Metabolomics is available to view or download in PDF. R7632.pdf Tested metabolites are featured on Scripps Center for Metabolomics METLIN Metabolite Database. To learn more, visit sigma.com/metlin.