Description
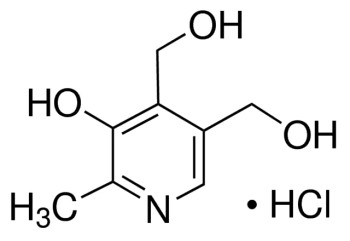
Pyridoxine hydrochloride
meets USP testing specifications
Synonym(s):
Adermine hydrochloride, PN HCl, Pyridoxol hydrochloride, Vitamin B6 hydrochloride
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
C8H11NO3 · HCl
CAS Number:
58-56-0
Molecular Weight:
205.64
Beilstein/REAXYS Number:
3632435
EC Number:
200-386-2
MDL number:
MFCD00012807
eCl@ss:
34058008
PubChem Substance ID:
24898493
NACRES:
NA.21
PROPERTIES
biological source
synthetic (organic)
Quality Level
200
agency
USP/NF
meets USP testing specifications
assay
98.0-102.0% dry basis
form
powder
color
white
mp
214-215 °C (lit.)
application(s)
pharmaceutical (small molecule)
SMILES string
Cl[H].Cc1ncc(CO)c(CO)c1O
InChI
1S/C8H11NO3.ClH/c1-5-8(12)7(4-11)6(3-10)2-9-5;/h2,10-12H,3-4H2,1H3;1H
InChI key
ZUFQODAHGAHPFQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
General description
Vitamin B group is water-soluble and exists in six forms namely the pyridoxal, pyridoxine, pyridoxamine, pyridoxamine 5′-phosphate, pyridoxine 5′-phosphate and pyridoxal 5′-phosphate.[1] The food sources of vitamin B6 include grains, nuts, fruits, vegetables and meat.[2]
Application
Pyridoxine hydrochloride has been used to test its neuroprotective functionality in traumatic brain injury (TBI) rats.[3] It has also been used as a reference standard to quantify vitamin B6 in feed and digesta samples using high-performance liquid chromatography(HPLC).[4]
Biochem/physiol Actions
Pyridoxine plays a key role in metabolism both carbohydrates and amino acids.[2] It supports brain development and its deficiency levels may lead to depletion of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) levels.[5] Pyridoxine catalyzes the neurotransmitter biosynthesis like dopamine and serotonin.[5] Pyridoxine in excess or deficient may lead to neuropathy.[6]
SAFETY INFORMATION
pictograms
GHS05
signalword
Danger
hcodes
H318
pcodes
P280 - P305 + P351 + P338
Hazard Classifications
Eye Dam. 1
Storage Class
11 - Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
WGK 1
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
ppe
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)