Description
Creatine monohydrate
≥98%
-
CAS Number 6020-87-7
-
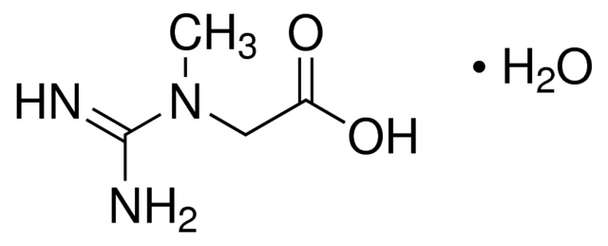
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation) C4H9N3O2 · H2O
-
Molecular Weight 149.15
-
Beilstein/REAXYS Number 7942755
-
EC Number 200-306-6
-
MDL number MFCD00071582
-
PubChem Substance ID 24892629
-
NACRES NA.26
Properties
| Related Categories | Aloe Vera, Cell Biology, Nutrition Research, Other Biochemical, Phytochemicals by Chemical Classification, |
| Quality Level | 200 |
| assay | ≥98% |
| form | powder |
| application(s) | cell culture | mammalian: suitable |
| color | white to off-white |
| mp | 292 °C |
| SMILES string | O.CN(CC(O)=O)C(N)=N |
| InChI | 1S/C4H9N3O2.H2O/c1-7(4(5)6)2-3(8)9;/h2H2,1H3,(H3,5,6)(H,8,9);1H2 |
| InChI key | MEJYXFHCRXAUIL-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Description
Application
Creatine (Cr) and phosphocreatine (PCr) are involved with rapid ATP production primarily in skeletal muscle tissue via the action of creatine kinase(s). Creatine may be used as a supplement to study its uptake mechanism and metabolism of action.
Packaging
1 kg in poly bottle
100 g in poly bottle
Biochem/physiol Actions
Creatine is a nitrogenous compound that acts as a high-energy reservoir for the rapid regeneration of ATP. Approximately 95% of creatine is found in skeletal muscle, primarily as phosphocreatine. Creatine can be acquired through dietary consumption or formed from L-arginine, glycine, and L-methionine in a multi-step reaction that occurs in the kidneys and liver. Creatine is then transported to muscle tissue. Creatine supplementation is used for the enhancement of sports performance, primarily by increasing muscle mass. Creatine is also being investigated as a treatment of neuromuscular diseases, where it may aid in neuroprotection and by improving the cellular bioenergetic state.